Table of Contents
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain, automation and AI are emerging as key trends shaping the next generation of decentralized applications (dApps). One project that aims to capitalize on this growing market is GraphLinq. This platform enables users to create dApps, launch tokens, build bots, and design AI agents—all without requiring extensive coding knowledge. Let’s dive deep into GraphLinq to analyze its core aspects, project team, token details, functionality, and overall potential.
What is GraphLinq?
At its core, GraphLinq is a no-code automation platform designed for blockchain interactions. It provides an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) where users can design and deploy AI-powered agents, dApps, and bots using a drag-and-drop interface. The platform supports multiple blockchains, making it a flexible solution for Web3 developers.
GraphLinq offers a variety of features, including:
- Building dApps: Easily design and deploy decentralized applications.
- Launching tokens: Create and manage new cryptocurrencies without technical expertise.
- AI Agents: Automate Web3 tasks with AI-powered agents.
- Bots: Develop and deploy trading and utility bots.
The platform is particularly appealing to businesses and developers looking for automation solutions in the crypto space.
Key Features of GraphLinq
GraphLinq IDE – A No-Code Blockchain Builder
One of the standout features of GraphLinq is its no-code IDE. This tool enables users to create blockchain applications using a simple drag-and-drop interface. It lowers the barrier to entry, making blockchain development more accessible to non-programmers.
AI-Powered Automation
GraphLinq integrates AI agents that help automate various blockchain tasks. These agents can be used for trading, analytics, and other Web3 applications. However, while AI in blockchain is a promising narrative, adoption and real-world use cases remain in early stages.
Cross-Chain Compatibility
GraphLinq supports multiple blockchains, allowing users to build cross-chain applications. This interoperability is crucial in today’s fragmented crypto landscape.
GraphLinq Marketplace
The GraphLinq Marketplace allows developers to buy and sell pre-built automation templates. This feature enables users to quickly deploy automation without building from scratch.
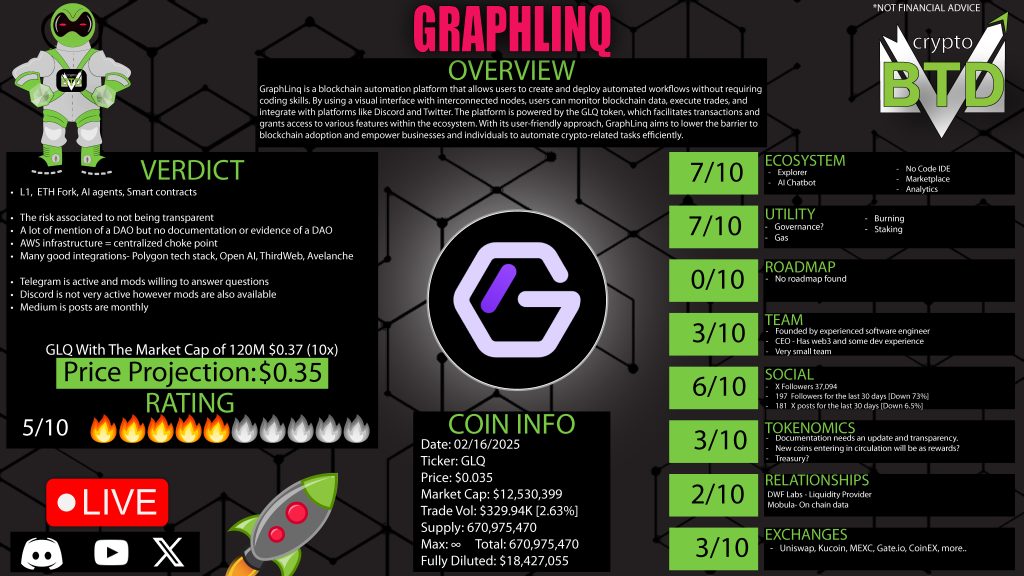
GraphLinq Chain & Token (GLQ)
GraphLinq operates its own blockchain, known as GraphLinq Chain, with GLQ as its native token. GLQ is used for:
- Paying gas fees for transactions.
- Staking for rewards.
- Governance (although details on the DAO remain unclear).
- Running AI agents and dApps.
While the tokenomics model is promising, some transparency issues exist regarding GLQ’s supply and distribution.
GraphLinq’s Role in the Evolving Blockchain Ecosystem
Bridging Web2 and Web3
One of GraphLinq’s primary goals is to make blockchain technology accessible to Web2 users and businesses. By providing a no-code platform, it lowers the technical barriers that often prevent companies from adopting blockchain solutions. This could position GraphLinq as a critical bridge between traditional businesses and decentralized applications.
Potential Use Cases
GraphLinq’s automation and AI capabilities open doors to various applications, including:
- Crypto Trading Bots: Automating trading strategies without needing coding skills.
- DeFi Automation: Managing yield farming, liquidity provision, and lending protocols.
- Data Analytics: Real-time blockchain analytics for businesses.
- NFT Marketplaces: Enhancing NFT trading and auction automation.
These use cases highlight the platform’s versatility, but its success depends on user adoption and further ecosystem development.
Competitive Landscape
GraphLinq competes with other blockchain automation and AI projects like Chainlink (oracles), The Graph (data indexing), and Moralis (Web3 development tools). However, its no-code approach gives it a unique advantage in appealing to non-technical users and businesses looking to enter the blockchain space.
Concerns & Challenges
1. Lack of Transparency in Tokenomics
One of the biggest concerns surrounding GraphLinq is the lack of detailed transparency in its tokenomics. The website and documentation provide limited information on token distribution, vesting schedules, and governance. For investors, this ambiguity presents a risk factor.
2. Limited Adoption & Ecosystem Growth
The GraphLinq Marketplace has very few active projects, raising questions about real-world adoption. Without a strong user base, even the most well-built platforms can struggle to gain traction.
3. Centralized Infrastructure (AWS Dependency)
Despite branding itself as a decentralized project, GraphLinq relies on AWS (Amazon Web Services) for its backend infrastructure. This creates a centralized choke point, which contradicts the principles of decentralization that blockchain projects aim to uphold.
4. Small Development Team
GraphLinq’s team appears small, and the original founder is no longer actively leading the project. The current CEO has relevant experience, but questions remain regarding the project’s long-term leadership and development efforts.
5. No Clear Roadmap
A major red flag for any crypto project is the lack of a public roadmap. Without a clear development plan, investors and developers have no visibility into future milestones or expected progress.
Final Thoughts
GraphLinq presents a speculative opportunity with potential benefits and risks. While its concept and technology have promise, the project currently lacks transparency, widespread adoption, and a clear development plan.
Advantages of GraphLinq:
✅ No-code platform makes blockchain development more accessible.
✅ AI-powered automation aligns with growing trends in Web3.
✅ Cross-chain functionality increases usability.
✅ Low market cap allows room for potential growth.
Disadvantages of GraphLinq:
❌ Unclear details on token distribution and governance.
❌ Limited real-world adoption and user engagement.
❌ Dependence on centralized infrastructure raises concerns.
❌ Small team with uncertain long-term direction.
❌ Lack of a clear roadmap for future development.
GraphLinq remains an early-stage project that requires careful observation. If the team improves transparency, fosters adoption, and enhances decentralization, the project could gain momentum.
What are your thoughts on GraphLinq? Join the discussion below!







0 Comments